Notebooks
Taiao Case 4
Description:
-
Metadata:
Author:
N/A
Licenses:
None
Datasets:
Content:
We load the required libraries used to train the LSTM
import tensorflow as tf import tensorflow.keras as keras import tensorflow.keras.backend as K from tensorflow.keras.layers import LSTM from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing.sequence import TimeseriesGenerator import pandas as pd import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as pyplot
The flood prediction dataset has been encapsulated in the packages below and can be loaded using the code below
import taiao.dataset.river as data import taiao.visualization.river as visualiser import taiao.model.river as models
pd.DataFrame(xTrain).tail()
We set the hyper-parameters and load the dataset and create the keras data generator
forecast=12
lookback=288
xTrain = data.x('train',forecast)
yTrain = data.y('train',forecast)
xTest = data.x('test',forecast)
yTest = data.y('test',forecast)
trainGen=TimeseriesGenerator(xTrain,yTrain,length=lookback,batch_size=3)
testGen=TimeseriesGenerator(xTest,yTest,length=lookback,batch_size=1)
featureCount=xTrain.shape[1]
depth=2Here we define the model and train the output
model = models.LSTM(depth,featureCount,lookback, optimizer="adam") history = model.fit(trainGen,validation_data=testGen, epochs=1).history model.save('3DLookBack_3hr_forecast_rmse')
134315/134322 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.0027
We now evaluate the model
model.evaluate(testGen) trainPredict = model.predict(trainGen) testPredict = model.predict(testGen)
172522/172522 [==============================] - 469s 3ms/step - loss: 9.9911e-04
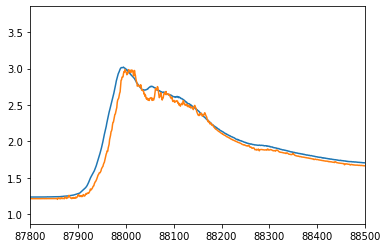
and plot the output for the flood event of interest
pyplot.plot(yTest[lookback:]) pyplot.plot(testPredict) pyplot.xlim((87800,88500)) pyplot.show(block=False)
We do a dump of the csv file comparing the predicted river level to the actual river level
CsvTemp=np.concatenate([yTest[lookback:].reshape(-1,1),testPredict],axis=1) np.savetxt('3D_Prediction_3hr_rmse.csv',CsvTemp,delimiter=',')
